Artificial Intelligence (AI)-Driven Smart City Infrastructure: A Guide for Policymakers
Smart cities are increasingly being seen as a way to improve the quality of life for residents, attract businesses, and reduce costs. By using AI and other advanced technologies, smart cities can collect and analyze data to improve traffic flow, energy efficiency, public safety, and more.

However, there are also a number of challenges associated with developing and implementing AI-driven smart city infrastructure. These include concerns about data privacy, security, and bias. Policymakers need to be aware of these challenges and take steps to mitigate them in order to ensure that smart cities are developed in a way that benefits everyone.
This guide provides an overview of AI-driven smart city infrastructure, the benefits and challenges associated with it, and the policy implications of developing and implementing this technology.
What is an AI-Driven Smart City?

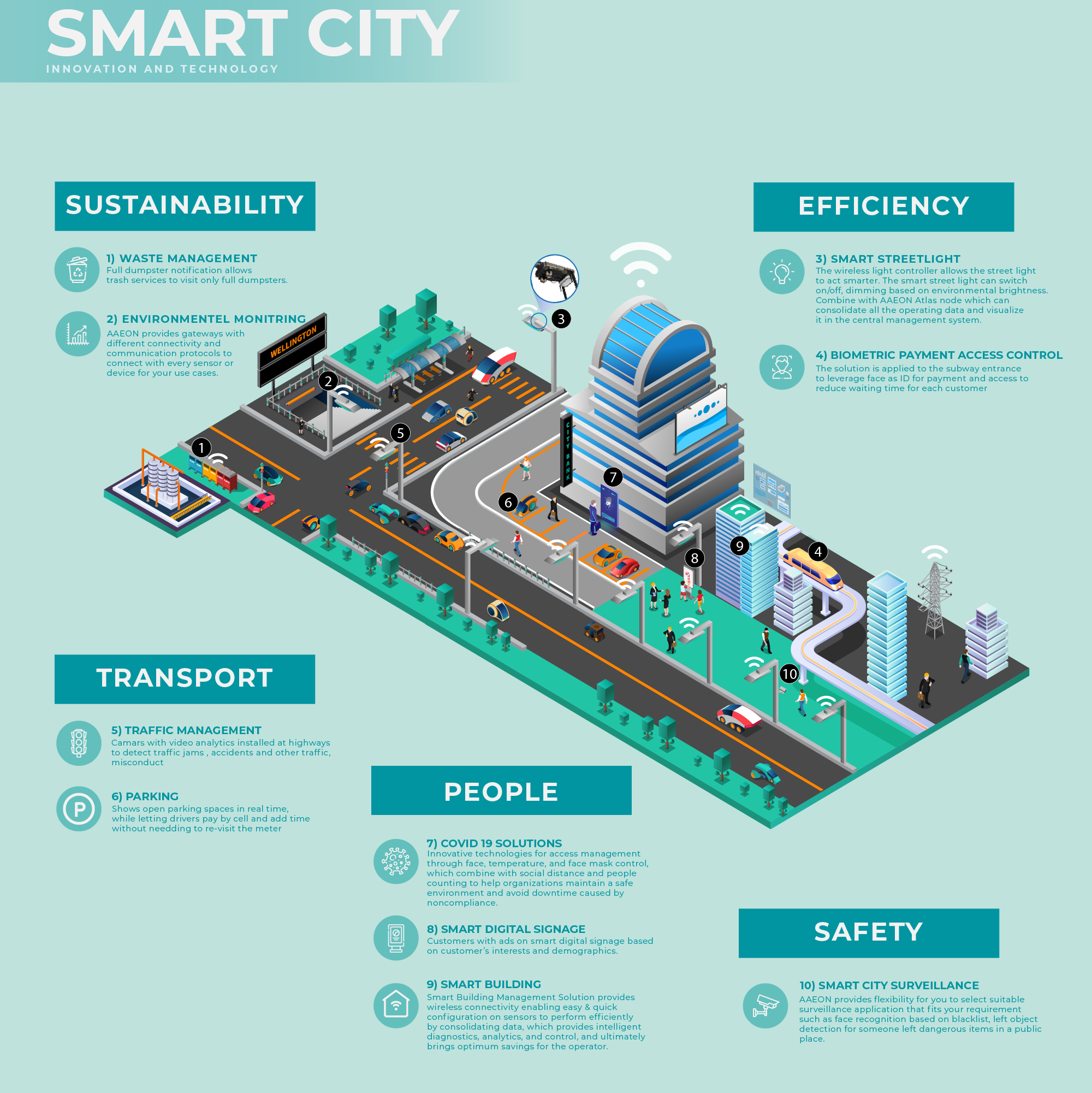
A smart city is a city that uses technology to improve the quality of life for its residents. This can include using sensors to collect data on traffic flow, air quality, and public safety, and using AI to analyze this data to make better decisions. For example, a smart city might use AI to optimize traffic flow by rerouting traffic around accidents or construction zones, or to predict and prevent crime by identifying patterns of criminal activity.
AI-driven smart cities are a step up from traditional smart cities in that they use AI to not only collect and analyze data, but also to make decisions and take actions. This can give smart cities the ability to respond to problems more quickly and effectively, and to make improvements that are more tailored to the needs of their residents.
Benefits of AI-Driven Smart Cities

There are a number of potential benefits to using AI to drive smart city infrastructure. These include:
- Improved traffic flow: AI can be used to collect data on traffic flow and use this data to optimize traffic signals and routes. This can help to reduce congestion and improve travel times.
- Energy efficiency: AI can be used to monitor energy usage and identify ways to reduce it. This can help cities save money on their energy bills and reduce their environmental impact.
- Public safety: AI can be used to monitor crime rates and identify patterns of criminal activity. This can help law enforcement officials to prevent crime and keep residents safe.
- Environmental sustainability: AI can be used to monitor air quality and water quality, and to identify ways to improve them. This can help cities to reduce their environmental impact and improve the quality of life for their residents.
- Social equity: AI can be used to identify and address social problems, such as poverty, homelessness, and discrimination. This can help to create more inclusive and equitable cities.
Challenges of AI-Driven Smart Cities

While AI-driven smart cities offer a number of potential benefits, there are also a number of challenges associated with this technology. These include:
- Data privacy: AI-driven smart cities collect a lot of data on their residents, and this data can be used for a variety of purposes. This raises concerns about data privacy and the potential for this data to be misused.
- Security: AI-driven smart cities rely on complex computer systems, and these systems are vulnerable to cyberattacks. This could potentially allow criminals to access sensitive data or disrupt critical city services.
- Bias: AI algorithms can be biased against certain groups of people, such as people of color or women. This can lead to decisions that are unfair or discriminatory.
- Cost: Developing and implementing AI-driven smart city infrastructure is expensive. This can make it difficult for smaller cities or cities with limited resources to adopt this technology.
Policy Implications of AI-Driven Smart Cities
The policy implications of AI-driven smart cities are complex and far-reaching. Policymakers need to consider a number of factors when developing policies for this technology, including:
- Data privacy: Policies need to be in place to protect the privacy of data collected by smart cities. This includes ensuring that data is only used for its intended purpose and that it is not shared with third parties without the consent of the individual.
- Security: Policies need to be in place to protect smart city systems from cyberattacks. This includes measures such as encryption, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems.
- Bias: Policies need to be in place to prevent AI algorithms from being biased against certain groups of people. This includes measures such as auditing algorithms for bias and using human oversight to review decisions made by AI systems.
- Cost: Policies need to be in place to ensure that AI-driven smart city infrastructure is affordable for cities of all sizes. This could include providing financial assistance to cities that want to adopt this technology.
Conclusion


AI-driven smart cities offer a number of potential benefits, but there are also a number of challenges associated with this technology. Policymakers need to be aware
Post a Comment